Butt Welding Machines

160 Manual Hydraulic Plastic
Pipe Butt Welding Machine
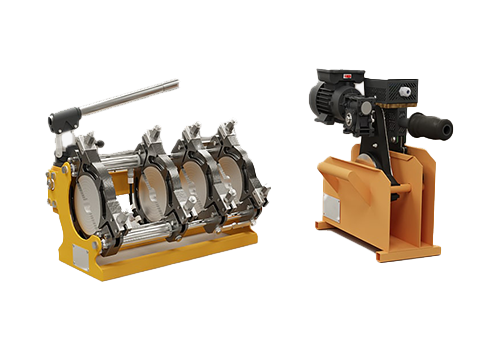
160 Manual Hydraulic Plastic
Pipe Butt Welding Machine

160 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine
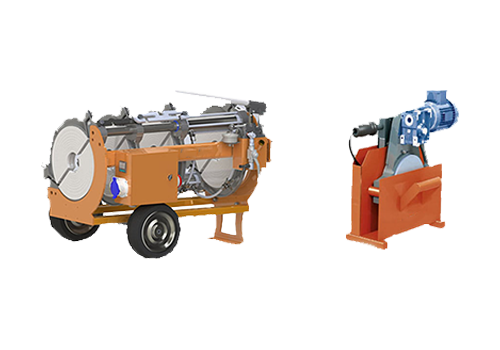
250 Manual Hydraulic Plastic
Pipe Butt Welding Machine

250 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine
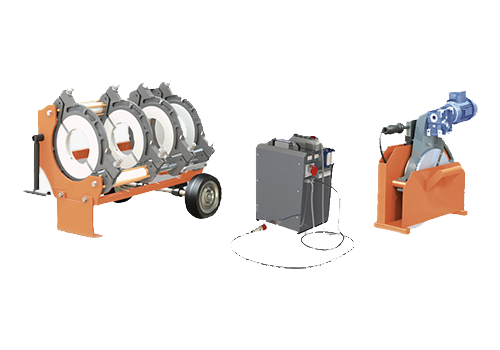
315 Manual Hydraulic Plastic
Pipe Butt Welding Machine
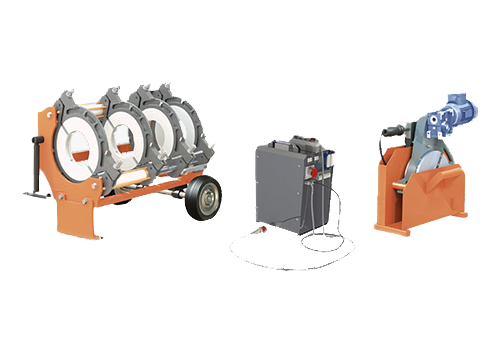
315 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine
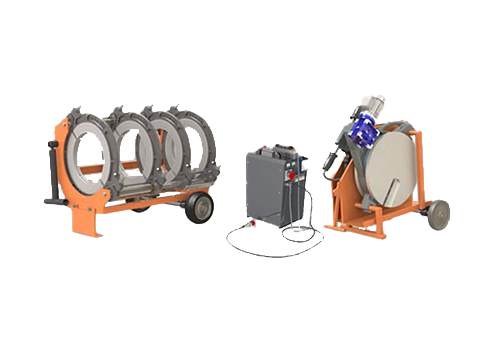
400 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine

400M Single-Phase Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine

500 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine

630 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine

800 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine

1000 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine

1200 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine

1600 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine
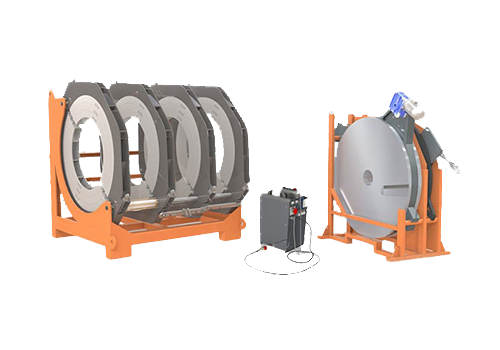
2000 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine
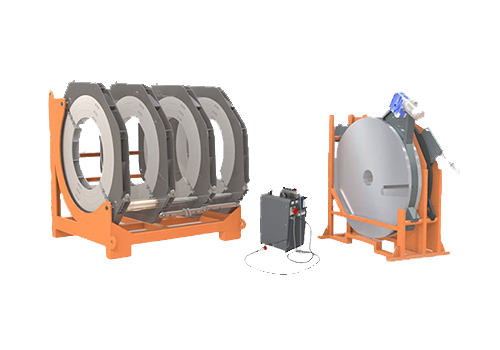
2500 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine
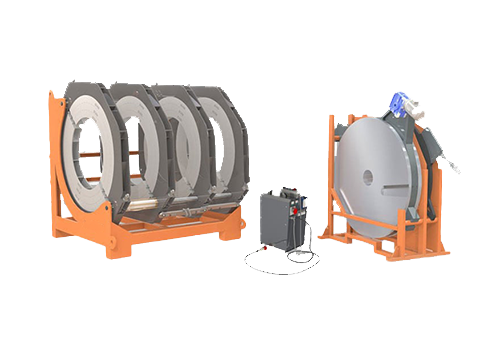
2800 Hydraulic Plastic Pipe Butt Welding Machine
Main Frame
The main frame of a butt-welding machine is fitted with two fixed and two movable clamps that support, fix and centre the plastic pipes to be welded. A hydraulic pressure force is applied to the system; two pistons mounted on the guide shaft drive the movable clamps back and forth, providing the motion required for the welding process.
Facing Tool (Trimmer)
The facing tool has two rotating blades—one on each side—each fitted with cutting knives. Before heating, it squares and cleans the pipe ends that have already been clamped and centred on the main frame, preparing them for fusion. The rotational movement is generated by an integrated motor–gearbox assembly.
Heater Plate
After facing, the heater plate warms the pipe ends to the specified roughness, readying them for fusion. The temperature is set with the thermostat located on the heater itself.
Protection & Support Box
The protection/support box prevents heat loss from the heater plate and shields both the heater and facing tool from external impacts (shock, water, etc.).
Commissioning the Machine & Performing a Weld
Power-up
• Plug the electrical unit into a generator or any 220 V–380 V outlet.Pre-heat the heater plate
• Insert the heater plug into the control panel, switch on and allow it to reach temperature.Check clamp travel
• Use the operating lever to move the movable clamp group fully forward and back, confirming smooth motion.Select inserts
• Choose clamp inserts (reducers) to match pipe diameter and mount the pipes, leaving clearance for facing.Install the facing tool
• Remove the facing tool from its box, place it on the guide shafts of the main frame and secure the safety pin.Face the pipe ends
• Plug the facing tool into the electrical unit, press the start button, and—after ensuring ice is melted in cold weather—rotate the lever clockwise to feed the movable clamps toward the running facing tool.
• Continue until both pipe ends are flat and smooth; maintain facing pressure between 20 – 60 bar.Remove the facing tool
• Unplug it and return it to its compartment.Verify heater temperature
• Check that the heater has reached the set fusion temperature (refer to temperature table “T.01”).Insert the heater plate
• Place the plate on the guide shafts.Initial heating (bead formation)
• Bring the pipe ends against the PTFE-coated heater surface. Using the material/diameter table, apply the required fusion force to obtain the specified bead thickness (first-heat stage).Soak heating (heat-without-force)
• After bead thickness is achieved, release pressure and continue heating for the time given in the table.Remove heater plate
• Open the clamps counter-clockwise, remove the heater, and place it back in its box.Fusion
• Immediately apply the fusion force (identical to the initial heating force) and press the pipe ends together.Cooling
• Keep the joint under clamp pressure for the cooling time specified in the table.Completion
• The weld is now finished. In CNC models the total fusion pressure is calculated automatically.
Use SHELL 46 hydraulic oil.
Advantages of HDPE Pipe Butt-Welding Machines
Rapid, leak-tight joints – Achieve strong, pressure-tight welds in far less time than conventional methods, ideal for large-scale water or gas pipelines.
No extra fittings – Designed specifically for HDPE, they create a reliable bond between two pipe sections without costly couplings.
High precision – The machine aligns both pipe ends perfectly before fusion, ensuring joint strength and correct orientation.
Automated control – Integrated controls make operation consistent and straightforward.
Cost-effective & user-friendly – Minimal setup, can be run by a single operator, and competitively priced, suiting small projects as well.
Portable – Lightweight construction allows easy transport between job sites—perfect for contractors welding HDPE pipe in multiple locations.



 BİZE YAZIN
BİZE YAZIN